Settings
The permission manager can be accessed from the Global actions menu under Administration > Permissions. This link loads the page Special:PermissionManager.
There are four different permission settings. The default setting is "Private wiki". If you want to grant different permissions in different namespaces, the setting "Custom setup" is required.

An administrator can choose between four types of settings. The setting Private Wiki is activated by default.
| Permission type | Description | Special permissions |
|---|---|---|
| Public wiki | The wiki is visible to and editable by anyone, including anonymous users (that means users that are not logged in).
|
Sonderverrechtung: [1]// Anonymous and logged-in users can read and edit
$this->groupRoles['*']['reader'] = true;
$this->groupRoles['*']['editor'] = true;
|
| Protected wiki | The wiki is visible to anyone. Only logged-in users can edit the wiki.
|
Sonderverrechtung:[1]:// Anonymous users can read, logged-in users can edit
$this->groupRoles['*']['reader'] = true;
$this->groupRoles['*']['editor'] = false;
$this->groupRoles['user']['editor'] = true;
|
| Private wiki | Only logged-in users can view and edit the wiki.
|
Sonderverrechtung:[1]// Only logged-in users can read. The group "editor" has to be manually assigned to users.
$this->groupRoles['*']['reader'] = false;
$this->groupRoles['*']['editor'] = false;
$this->groupRoles['user']['reader'] = true;
$this->groupRoles['user']['editor'] = false;
$this->groupRoles['editor']['editor'] = true;
$this->groupRoles['sysop']['editor'] = true;
|
| Custom setup
(BlueSpice pro) |
Roles and groups are assigned by an administrator. This is necessary if different namespaces need to have different user rights. See the next section for more info. |
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Global permissions (modified by the special permissions shown in the table above):
'bureaucrat' => [ 'accountmanager' => true ], 'sysop' => [ 'reader' => true, 'editor' => true, 'reviewer' => true, 'admin' => true ], 'user' => [ 'editor' => true ], 'editor' => [ 'reader' => true, 'editor' => true ], 'reviewer' => [ 'reader' => true, 'editor' => true, 'reviewer' => true
About role-based permissions
Roles represent a collection of individual permissions that are necessary to perform certain functions in the wiki. For example, for a user who is supposed to only read the wiki, many permissions in addition to the "read" permission are needed: The ability to change their own settings, to search the wiki, to view page ratings, and so on.
All permissions that make up a logical group are encapsulated in a role, in this example the role "reader". If wiki administrators want to grant read-only rights to a user group, they only need to assign that group the "reader" role, instead of assigning many individual permissions that are needed to create a "read"-user.
By assigning roles to a group, all users belonging to that group receive the rights of these roles. Roles are never assigned directly to users, but always to groups instead. Users are then assigned to one or more groups.
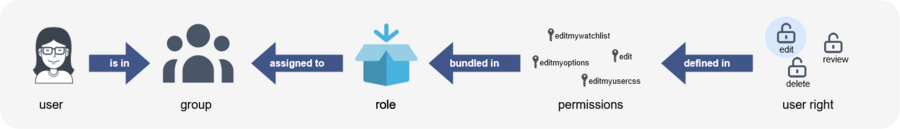
As a result, the following administration pages play a role in the rights management:
- Namespace manager: In the wiki, user groups can be granted different permissions via roles in individual namespaces.
- User manager: Individual users are assigned to groups to obtain the permissions associated with the group.
- Permission manager (with integrated group manager): In the Permission manager, the user groups are managed and assigned to their roles in the namespaces.
The following elements are part of the rights system:
| Function |
|---|
| Enables a specific action |
| Combination of rights (rights can only be granted via roles) |
| Entity in the wiki instance database. Has a unique user name and a unique user ID. |
| A collection of users. A user is assigned to one or more groups. There are system-internal groups (which cannot be removed or renamed) and custom groups. In the case of custom groups, the group name often consists of the role and a namespace name. |
| Authorisations can be defined at namespace level. But generally not per page. |
Classic rights assignment procedure
| Step | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Namespace management | Create a namespace via the Special:NamespaceManager page.
|
| 2 | Group management | Create a user group for each role that you want to manage in this namespace via the Special:PermissionManager page. The group name should follow a specific pattern, e.g. <namespace_name>_<role_name>.
|
| 3 | Rights management | Connect groups, roles and namespaces with Special:PermissionManager . Simply follow the name pattern of the group.
|
| 4 | User management | Assign users to the groups. |
Custom setup
The "Custom setup" is used to assign global and namespace-specific permissions to groups.
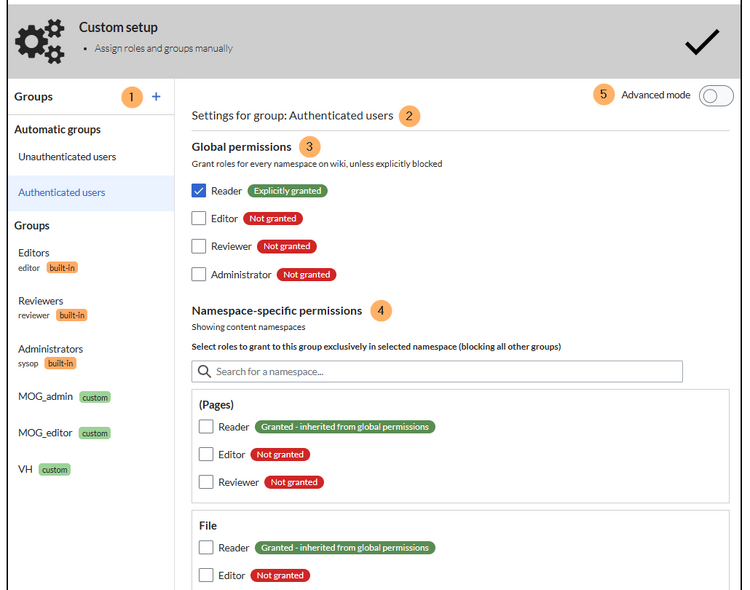
| Element | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Groups panel | This panel lists all groups in the wiki:
|
| 2 | Selected user group | The heading shows which group is currently selected for viewing or for setting the permissions. |
| 3 | Global permissions | You can grant global permissions that apply to the entire wiki for this group. If you want to only grant permissions in one or more specific namespaces, you do not need to select a role here. |
| 4 | Namespace-specific permissions | Shows a filterable list of all namespaces and their permissions for the selected user group.
If a change is saved here, the group must be selected again in the group list if the setting should be reviewed after saving. |
| 4 | Advanced mode | This view displays the roles of a user group in a matrix format. The role names are clickable and show the individual permissions within a role. |
Creating custom groups
Groups can be created from the permission manager page to support the following scenarios:
- Unique permissions for different namespaces: If pages in the wiki should have different permissions than other pages, they need to be located in different namespaces.
- Page access: The purpose of the page access functionality is to override the permissions set on the namespace-level and are usually only used as exceptions. Page-level permissions are difficult to maintain and contradict the namespace-based permissions model.
- Workflows: Workflow tasks can be assigned to user groups.
- Page assignments: Pages can be assigned to groups as well as to individual users.
Advanced mode
The permission manager consists of the group tree (1) and the role matrix (2). Namespaces can be added and removed as needed (3):
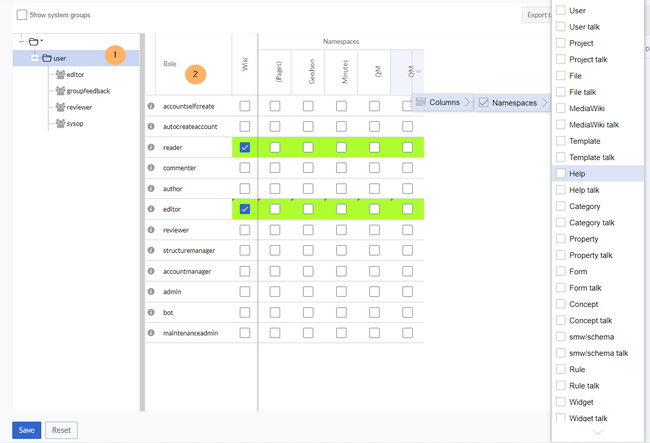
The group tree on the left displays all groups. The following groups are available by default:
- Automatically created groups:
- Unauthenticated users: All non-logged-in users (anonymous users) belong to this group.
- Authenticated users: The default group for all logged-in users, even if they don't belong to a subgroup. Permissions are inherited from this group to the groups.
- Groups: These groups first inherit permissions from the automatically created groups. The inherited permissions can be overridden here.
- Built-in groups: These groups are generic and used across namespaces in the wiki.
- Custom groups: Additional groups created by administrators using the corresponding link (+ symbol at the top of the list).
The columns in the role matrix:
- Role name: The role(s) assigned to a group in specific namespaces to grant user permissions. Clicking on the name displays all permissions assigned to that role.
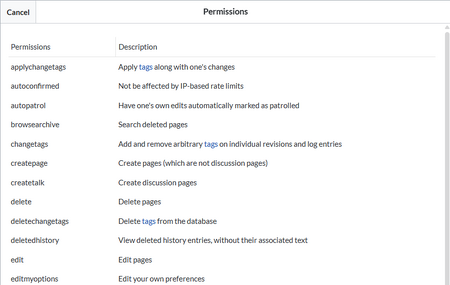
Permissions in the role "editor"
- Wiki: Assignment of a role to the entire wiki. By assigning the role in this column, a user group gets permissions in this role on the wiki (all namespaces).
- Individual namespaces:
- Roles can be assigned within namespaces. If a group in a namespace is explicitly assigned a role, all other groups lose the permissions for that role and must be explicitly reassigned if desired.
- Multiple groups can be assigned one or more roles for a namespace.
- The display of additional namespaces can be controlled using the "Namespaces" filter above the matrix view.
Role inheritance
All roles assigned to the "unauthenticated users" group are inherited by the "authenticated users" group. All roles explicitly assigned to the "authenticated users" group are inherited by the custom groups. If a group inherits the role from an automatic group in the role matrix, this is displayed in green. In this case, a check mark is not explicitly set.
Explicitely set namespace permissions
If a group is explicitly assigned a specific role in a namespace, that role is automatically revoked from all other groups. In the following example, the read permission in the Training namespace is assigned to the Administrator group:

All other groups no longer have access to this namespace. In the standard view, this is displayed as "denied":
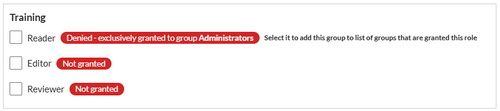
To extend access to other groups, these different groups must be clicked and the checkboxes in the "Training" namespace must be explicitly selected.
In the "Advanced Mode" view, the namespace is grayed out if access is denied:
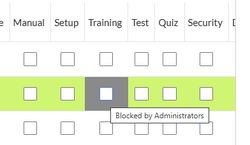
Default roles
By default, the permission manager offers a number of predefined roles. The following roles are primarily used:
- reader: basic read access. Users can also edit their personal settings
- editor: create content, edit and delete content
- reviewer: if you have activated the review function and, therefore, work draft pages in a namespace, there must be at least one group with the role of reviewer. By default, the group “reviewer” is available for this purpose. Only users in the reviewer role can approve draft pages. Reviewers generally need read, write and review rights via the corresponding three roles of reader, editor and reviewer. However, if you have not activated the review function in any namespace, you do not need this role in your wiki
- admin: grants access to all administrative special pages and to all typical administrative features
The following roles can be assigned via the Advanced Mode in addition:
- commenter: allows the creation of discussion contributions and page ratings, but not of the pages themselves. The editor role includes all the rights of the commenter role. If a group has editor rights, it does not need special commenter rights
- accountselfcreate: allows signing in via a connected authentication mechanism (Single-sign on)
- author: all permissions necessary for creating content on the wiki. Editing, moving, or deleting pages is not possible
- structuremanager: allows some actions for wiki maintenance such as moving pages, mass deleting pages or searching and replacing text, as well as renaming namespaces
- accountmanager: enables the administration of user accounts. Since user accounts are managed independently of namespaces in the wiki, this role cannot be restricted to individual namespaces. Grayed-out namespaces have no meaning here as long as the role in the wiki itself is highlighted in green
- bot: exists to achieve recurring system actions. This role is assigned to the user BSMaintenance in Bluespice via the group bot. The group bot should not be changed
- maintenanceadmin: similar to the admin role, but with extended admin rights for maintaining wiki integrity
Restricting read permissions
It is possible to limit read permissions in a namespace by explicitely assigning the role reader to one or more particular groups. When users in other groups try to access a page in such a namespace, they will get a message that the permissions are denied.
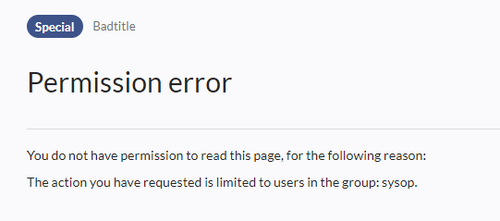
While a user cannot access the content of the page, the wiki still shows links to these pages to all users in some contexts, even if a user does not have permissions to access the page content itself.
The following lists show which extensions or functionalities do not show links to restricted pages — because they are permissions-aware — and where the links are shown regardless of permissions.
Exensions that are permissions-aware
Query results and page lists provided by the following extensions do not show links to pages to which the current user has no access on the namespace level:
- ExtendedSearch (and functionality based on Extended Search in general, e.g. TagSearch, ExtendedFilelist).
- Semantic MediaWiki
- TopList
Extensions and special pages that are not permissions-aware
Extensions that provide page lists and that do not hide links to read-restricted pages to the affected users. Examples:
- DynamicPageList3
- SmartList
- WatchList (both the tag and the special page)
In general, all MediaWiki special pages do not check permissions and therefore list these pages for the affected users. Most common examples:
- Special:RecentChanges
- Special:Bookshelf (Note: If this is an issue, you can limit access to the namespace Book to selected groups. The page Special:Bookshelf then won't show any links to books to users who do not have access to the Book namespace. Links to individual books can then be provided on various portal pages as needed).
- Category pages: All pages in the namespace Category
Limited transclusion
If you explicitely assign the reader role (or any other role that contains the read permission) in a namespace to a group or groups, that namespace is automatically configured so that its content cannot be transcluded. This is for security reasons, since MediaWiki does not check permissions when transcluding content.
Technical info
Logging
Every change to the roles is logged in Special:Log, in the Permission Managerlog .
These logs are available only to wiki administrators (users in groups with the role admin).
Related info
